Introduction
Infectious diseases have long been a concern for global health, affecting millions of people each year. These diseases are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites that invade the body and lead to illness. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and learning prevention methods are key to protecting yourself and others from infectious diseases. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of infectious diseases, their common symptoms, and the most effective prevention strategies to stay healthy.
Definition
Infectious diseases are illnesses brought on by pathogenic microorganisms as parasites, fungus, viruses, or bacteria. These bacteria are easily transferred from one person to another through a variety of channels, including direct touch, tainted food or water, and even the air. TB, COVID-19, the flu, and the common cold are common examples. In order to stop its spread, prevention strategies like immunization, good personal hygiene, and avoiding direct contact with sick people are crucial.
What Are Infectious Diseases?
Infectious diseases are illnesses caused by harmful microorganisms that enter the body and disrupt normal functioning. Unlike non-infectious diseases, such as diabetes or cancer, infectious diseases can be transmitted from person to person, animal to person, or even from contaminated environments.
The agents responsible for infectious diseases include:
Bacteria – Single-celled organisms that can multiply quickly and release toxins, which are harmful to the body. Examples of bacterial infections include tuberculosis, strep throat, and urinary tract infections.
Viruses – Much smaller than bacteria, viruses require a host cell to multiply. Once inside a host, they can hijack cells to replicate and spread. Viral infections include influenza, HIV, and the common cold.
Fungi – Microorganisms that can cause infections, particularly in the skin, lungs, and other tissues. Examples include athlete’s foot and yeast infections.
Parasites – Organisms that live in or on a host organism and derive nutrients at the host’s expense. Malaria and toxoplasmosis are examples of diseases caused by parasites.
Each of these pathogens has distinct characteristics and methods of transmission, which influence how infectious diseases spread and how they can be managed.
How Infectious Diseases Spread
Infectious diseases can spread through various modes, including:
- Direct Contact: Physical contact with an infected person can transfer pathogens, as seen with respiratory illnesses or skin infections.
- Indirect Contact: Pathogens can survive on surfaces like doorknobs, handles, or shared objects, and people can contract infections by touching these surfaces.
- Airborne Transmission: Some infections, like the flu or COVID-19, spread through droplets expelled when an infected person sneezes or coughs, which can linger in the air and infect others who breathe them in.
- Vector-Borne Transmission: Certain diseases are spread through insects like mosquitoes or ticks, which carry the pathogen from one host to another, as in malaria and Lyme disease.
- Food and Water: Infections like salmonella and cholera can spread through contaminated food or water sources.
Understanding the modes of transmission helps in identifying effective prevention strategies and minimizing the spread of these diseases.
Common Symptoms of Infectious Diseases
Symptoms of infectious diseases vary depending on the type of pathogen and the body’s response. However, many infections present similar symptoms, making it challenging to identify the exact cause without proper testing.
Typical symptoms include:
Fever: A common response to infection, fever is the body’s way of fighting pathogens by raising the body temperature to make it less hospitable to invaders.
Fatigue: Infectious diseases often cause fatigue as the body redirects energy to the immune system to fight off the infection.
Muscle Aches: A common symptom in viral and bacterial infections, muscle aches may be due to inflammation as the immune system responds to infection.
Cough and Sore Throat: Respiratory infections like colds, the flu, and COVID-19 often include coughing and sore throat due to the irritation of the respiratory tract.
Diarrhea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal infections can cause digestive symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as pathogens disrupt the gut.
Skin Rashes: Some infections cause rashes or other skin changes, like redness, swelling, or irritation, as in chickenpox or measles.
While many infections resolve with rest and symptomatic treatment, severe infections may lead to complications if left untreated. Consulting a healthcare provider for persistent or worsening symptoms is important to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Prevention Strategies for Infectious Diseases
Preventing infectious diseases requires a combination of personal hygiene, environmental measures, and sometimes medical intervention. Here are some essential prevention strategies:
Practice Good Hygiene:
- Handwashing: Regular handwashing with soap and water is one of the simplest yet most effective ways to prevent infections. Wash your hands for at least 20 seconds, especially after using the restroom, before eating, and after touching shared surfaces.
- Respiratory Etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when you cough or sneeze to prevent respiratory droplets from spreading.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Pathogens can enter the body through the eyes, nose, and mouth, so avoid touching your face to reduce the chance of infection.
Vaccination:
- Vaccines are critical tools for preventing certain infectious diseases. Immunizations work by priming the immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens without causing illness.
- Vaccines have led to the near-eradication of diseases like polio and measles and remain essential for preventing seasonal flu and other viral infections.
Safe Food and Water Practices:
- Proper food handling and cooking can prevent foodborne infections. Ensure that foods are thoroughly cooked, especially meat, and avoid consuming raw or undercooked items.
- Drink clean, safe water and avoid unregulated sources that may be contaminated with pathogens.
Use of Protective Equipment:
- In certain situations, such as in healthcare settings or during outbreaks, wearing masks, gloves, or other personal protective equipment (PPE) can reduce the risk of transmission.
- Masks are particularly effective in reducing the spread of respiratory diseases by trapping droplets.
Environmental Control:
- Vector control, like eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed, helps prevent vector-borne diseases such as malaria or dengue.
- Maintaining clean and disinfected surfaces in communal or high-traffic areas can help reduce the spread of infections.
Healthy Lifestyle and Immune Support:
- A strong immune system can help the body fend off infections more effectively. A balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management contribute to overall health and immunity.
Seeking Medical Attention and Treatment
While many infectious diseases are mild and self-limiting, others can be severe and require medical intervention. If you experience symptoms such as high fever, difficulty breathing, persistent vomiting, or unexplained rashes, seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Physical Examination: Doctors may assess symptoms and physical signs like rashes or swollen lymph nodes.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests, cultures, or imaging can identify specific pathogens.
- Antibiotic or Antiviral Therapy: Depending on the type of infection, doctors may prescribe antibiotics (for bacterial infections) or antivirals (for viral infections). It’s crucial to complete the prescribed course to prevent resistance.
Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the spread of infectious diseases.
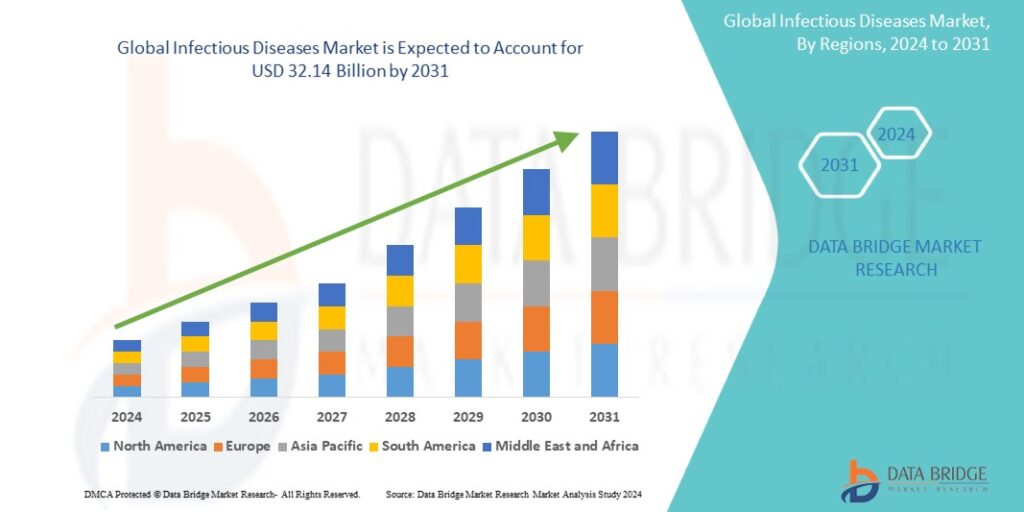
Growth Rate of Infectious Diseases Market
The global infectious diseases market was valued at USD 20.52 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to USD 32.14 billion by 2031, with a 5.77% CAGR from 2024 to 2031.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-infectious-diseases-market
Conclusion
Infectious diseases are a constant challenge, but with proper knowledge and preventive practices, they can be effectively managed. Understanding how infections spread, recognizing symptoms early, and adopting preventive measures are vital to reducing the impact of infectious diseases on individuals and communities.